Microsoft Remote Desktop Unable To Connect
Fix: Remote Desktop can’t Connect to the Remote Computer for one of these Reasons. If the issue is with your Computer or a Laptop you should try using Restoro which can scan the repositories and replace corrupt and missing files. Remote Desktop cannot connect to the VDI-based remote computer after enabling Microsoft RemoteFX 3D Video Adapter.; 2 minutes to read; D; v; s; In this article. This article provides a solution to an issue where Remote Desktop can't connect to a Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI)-based remote computer.
This article helps you understand the most common settings that are used to establish a Remote Desktop session in an enterprise environment, and provides troubleshooting information for Remote desktop disconnected errors.
Original product version: Windows Server 2012 R2
Original KB number: 2477176
Note
This article is intended for use by support agents and IT professionals.
Remote Desktop Server
A Remote Desktop Session Host server is the server that hosts Windows-based programs or the full Windows desktop for Remote Desktop Services clients. Users can connect to an RD Session Host server to run programs, to save files, and to use network resources on that server. Users can access an RD Session Host server from within a corporate network or from the Internet.
Remote Desktop Session Host (RD Session Host) was formerly known as the Remote Desktop server role service, and Remote Desktop Session Host (RD Session Host) server was formerly known as Remote Desktop server.
Remote connections for administration
Remote Desktop supports two concurrent remote connections to the computer. You do not have to have Remote Desktop Services client access licenses (RDS CALs) for these connections.
To allow more than two administrative connections or multiple user connections, you must install the RD Session Host Role and have appropriate RDS CALs.
Symptom 1: Limited Remote Desktop session or Remote Desktop Services session connections
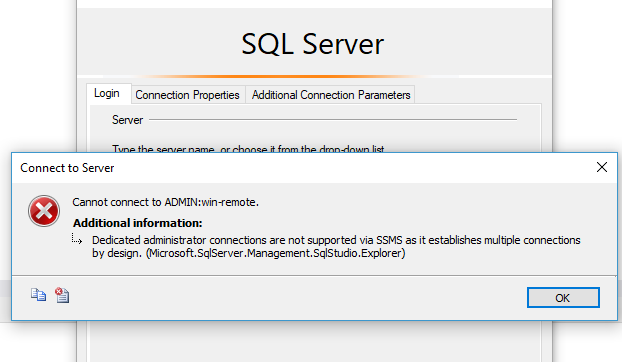
When you try to make a Remote Desktop Connection (RDC) to a remote computer or to a Remote Desktop server (Terminal Server) that is running Windows Server 2008 R2, you receive one of the following error messages:
Remote Desktop Disconnected.
This computer can't connect to the remote computer.
Try connecting again. If the problem continues, contact the owner of the remote computer or your network administrator.
Also, you are limited in the number of users who can connect simultaneously to a Remote Desktop session or Remote Desktop Services session. A limited number of RDP connections can be caused by misconfigured Group Policy or RDP-TCP properties in Remote Desktop Services Configuration. By default, the connection is configured to allow an unlimited number of sessions to connect to the server.
Symptom 2: Port assignment conflict
You experience a port assignment conflict. This problem might indicate that another application on the Remote Desktop server is using the same TCP port as the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP). The default port assigned to RDP is 3389.
Symptom 3: Incorrectly configured authentication and encryption settings
After a Remote Desktop server client loses the connection to a Remote Desktop server, you experience one of the following symptoms:
- You cannot make a connection by using RDP.
- The session on the Remote Desktop server does not transition to a disconnected state. Instead, it remains active even though the client is physically disconnected from the Remote Desktop server.
If the client logs back in to the same Remote Desktop server, a new session may be established, and the original session may remain active.
Also, you receive one of the following error messages:
Error message 1
Because of a security error, the client could not connect to the Terminal server. After making sure that you are logged on to the network, try connecting to the server again.
Error message 2
Remote desktop disconnected. Because of a security error, the client could not connect to the remote computer. Verify that you are logged onto the network and then try connecting again.
Symptom 4: License certificate corruption
Remote Desktop Services clients are repeatedly denied access to the Remote Desktop server. If you are using a Remote Desktop Services client to log on to the Remote Desktop server, you may receive one of the following error messages.
Error message 1
Because of a security error, the client could not connect to the Terminal server. After making sure that you are logged on to the network, try connecting to the server again.
Error message 2
Remote desktop disconnected. Because of a security error, the client could not connect to the remote computer. Verify that you are logged onto the network and then try connecting again.
Error message 3
Because of a security error, the client could not connect to the Terminal server. After making sure that you are logged on to the network, try connecting to the server again.
Remote desktop disconnected. Because of a security error, the client could not connect to the remote computer. Verify that you are logged onto the network and then try connecting again.
Additionally, the following event ID messages may be logged in Event Viewer on the Remote Desktop server.
Event message 1
Event message 2
Event message 3
Event message 4
Event message 5
Resolution for Symptom 1
To resolve this problem, use the following methods, as appropriate.
Verify Remote Desktop is enabled
Open the System item in Control Panel. To start the System tool, click Start, click Control Panel, click System, and then click OK.
Under Control Panel Home, click Remote settings.
Click the Remote tab.
Under Remote Desktop, select either of the available options, depending on your security requirements:
Allow connections from computers from computers running any version of Remote Desktop (less secure)
Allow connections from computers only from computers running Remote Desktop with Network Level Authentication (more secure)
If you select Don't allow connections to this computer on the Remote tab, no users will be able to connect remotely to this computer, even if they are members of the Remote Desktop Users group.
Verify Remote Desktop Services Limit number of connections policy
Start the Group Policy snap-in, and then open the Local Security Policy or the appropriate Group Policy.
Locate the following command:
Local Computer Policy > Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Connections Limit number of connections
Click Enabled.
In the RD Maximum Connections allowed box, type the maximum number of connections that you want to allow, and then click OK.
Verify Remote Desktop Services RDP-TCP properties
Follow these steps, depending on your operating system version.
Setting via Remote Desktop Services Configuration
Configure the number of simultaneous remote connections allowed for a connection:
On the RD Session Host server, open Remote Desktop Session Host Configuration. To open Remote Desktop Session Host Configuration, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, point to Remote Desktop Services.
Under Connections, right-click the name of the connection, and then click Properties.
On the Network Adapter tab, click Maximum connections, enter the number of simultaneous remote connections that you want to allow for the connection, and then click OK.
If the Maximum connections option is selected and dimmed, the Limit number of connections Group Policy setting has been enabled and has been applied to the RD Session Host server.
Verify Remote Desktop Services Logon rights
Configure the Remote Desktop Users Group.
The Remote Desktop Users group on an RD Session Host server grants users and groups permission to remotely connect to an RD Session Host server. You can add users and groups to the Remote Desktop Users group by using the following tools:
- Local Users and Groups snap-in
- The Remote tab in the System Properties dialog box on an RD Session Host server
- Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in, if the RD Session Host server is installed on a domain controller
You can use the following procedure to add users and groups to the Remote Desktop Users group by using the Remote tab in the System Properties dialog box on an RD Session Host server.
Membership in the local Administrators group, or equivalent, on the RD Session Host server that you plan to configure, is the minimum required to complete this procedure.
Add users and groups to the Remote Desktop Users group by using the Remote tab
Start the System tool. To do this, click Start, click Control Panel, click the System icon, and then click OK.
Under Control Panel Home, click Remote settings.
On the Remote tab in the System Properties dialog box, click Select Users. Add the users or groups that have to connect to the RD Session Host server by using Remote Desktop.
Note
If you select the Don't allow connections to this computer option on the Remote tab, no users will be able to connect remotely to this computer, even if they are members of the Remote Desktop Users group.
Add users and groups to the Remote Desktop Users group by using Local Users and Groups snap-in
- Click Start, click Administrative Tools, and then click Computer Management.
- In the console tree, click the Local Users and Groups node.
- In the details pane, double-click the Groups folder.
- Double-click Remote Desktop Users, and then click Add.
- In the Select Users dialog box, click Locations to specify the search location.
- Click Object Types to specify the types of objects that you want to search for.
- In the Enter the object names to select (examples) box, type the name you want to add.
- Click Check Names.
- When the name is located, click OK.
Note
- You can't connect to a computer that's asleep or hibernating, so make sure the settings for sleep and hibernation on the remote computer are set to Never. (Hibernation isn't available on all computers.) For information about making those changes, see Change, create, or delete a power plan (scheme).
- You can't use Remote Desktop Connection to connect to a computer using Windows 7 Starter, Windows 7 Home Basic, or Windows 7 Home Premium.
- Members of the local Administrators group can connect even if they are not listed.
Resolution for Symptom 2
Important
This section, method, or task contains steps that tell you how to modify the registry. However, serious problems might occur if you modify the registry incorrectly. Therefore, make sure that you follow these steps carefully. For added protection, back up the registry before you modify it. Then, you can restore the registry if a problem occurs. For more information about how to back up and restore the registry, seeHow to back up and restore the registry in Windows.
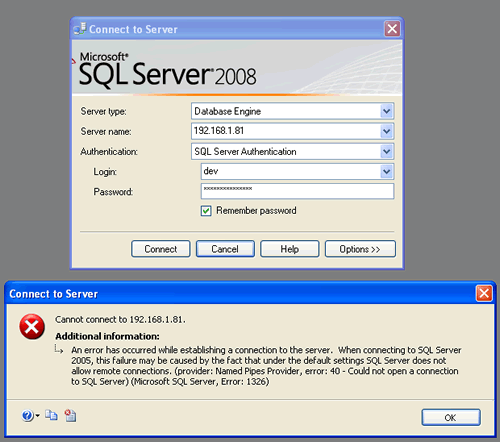
To resolve this problem, determine which application is using the same port as RDP. If the port assignment for that application cannot be changed, change the port assigned to RDP by changing the registry. After you change the registry, you must restart the Remote Desktop Services service. After you restart the Remote Desktop Services service, you should verify that the RDP port has been changed correctly.
Remote Desktop server listener availability
The listener component runs on the Remote Desktop server and is responsible for listening for and accepting new Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) client connections, thereby allowing users to establish new remote sessions on the Remote Desktop server. There is a listener for each Remote Desktop Services connection that exists on the Remote Desktop server. Connections can be created and configured by using the Remote Desktop Services Configuration tool.
To perform these tasks, refer to the following sections.
Determine which application is using the same port as RDP
You can run the netstat tool to determine whether port 3389 (or the assigned RDP port) is being used by another application on the Remote Desktop server:
- On the Remote Desktop server, click Start, click Run, type cmd, and then click OK.
- At the command prompt, type
netstat -a -oand then press Enter. - Look for an entry for TCP port 3389 (or the assigned RDP port) with a status of Listening. This indicates another application is using this port. The PID (Process Identifier) of the process or service using that port appears under the PID column.
To determine which application is using port 3389 (or the assigned RDP port), use the tasklist command-line tool along with the PID information from the netstat tool:
- On the Remote Desktop server, click Start, click Run, type cmd, and then click OK.
- Type
tasklist /svcand then press Enter. - Look for an entry for the PID number that is associated with the port (from the netstat output). The services or processes that are associated with that PID appear on the right.
Change the port assigned to RDP
You should determine whether this application can use a different port. If you cannot change the application's port, you must change the port that is assigned to RDP.
Important
We recommend that you do not change the port that is assigned to RDP.

If you have to change the port assigned to RDP, you must change the registry. To do this, you must be a member of the local Administrators group, or you must have been granted the appropriate permissions.
To change the port that is assigned to RDP, follow these steps:
On the Remote Desktop server, open Registry Editor. To open Registry Editor, click Start, click Run, type regedit, and then click OK.
If the User Account Control dialog box appears, verify that the action it displays is what you want, and then click Continue.
Locate and then click the following registry subkey:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlRemote Desktop serverWinStations
RDP-TCP is the default connection name. To change the port for a specific connection on the Remote Desktop server, select the connection under the WinStations key:
- In the details pane, double-click the PortNumber registry entry.
- Type the port number that you want to assign to RDP.
- Click OK to save the change, and then close Registry Editor.
Restart the Remote Desktop Services service
For the RDP port assignment change to take effect, stop and start the Remote Desktop Services service. To do this, you must be a member of the local Administrators group, or you must have been granted the appropriate permissions.
To stop and start the Remote Desktop Services service, follow these steps:
On the Remote Desktop server, open the Services snap-in. To do this, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Services.
If the User Account Control dialog box appears, verify that the action it displays is what you want, and then click Continue.
In the Services pane, right-click Remote Desktop Services, and then click Restart.
If you are prompted to restart other services, click Yes.
Verify that the Status column for the Remote Desktop Services service displays a Started status.
Verify that the RDP port has changed
To verify that the RDP port assignment has been changed, use the netstat tool:
On the Remote Desktop server, click Start, click Run, type cmd, and then click OK.
At the command prompt, type
netstat -athen press Enter.Look for an entry for the port number that you assigned to RDP. The port should appear in the list and have a status of Listening.
Important
Remote Desktop Connection and the Terminal server Web Client use port 3389, by default, to connect to a Remote Desktop server. If you change the RDP port on the Remote Desktop server, you will have to modify the port used by Remote Desktop Connection and the Remote Desktop server Web Client. For more information, see Change the listening port for Remote Desktop on your computer.
Verify that the listener on the Remote Desktop server is working
To verify that the listener on the Remote Desktop server is working correctly, use any of the following methods.

Note
RDP-TCP is the default connection name and 3389 is the default RDP port. Use the connection name and port number specific to your Remote Desktop server configuration.
Method 1
Use an RDP client, such as Remote Desktop Connection, to establish a remote connection to the Remote Desktop server.
Method 2
Use the qwinsta tool to view the listener status on the Remote Desktop server:
- On the Remote Desktop server, click Start, click Run, type cmd, and then click OK.
- At the command prompt, type qwinsta, and then press Enter.
- The RDP-TCP session state should be Listen.
Method 3
Use the netstat tool to view the listener status on the Remote Desktop server:
- On the Remote Desktop server, click Start, click Run, type cmd, and then click OK.
- At the command prompt, type
netstat -athen press Enter. - The entry for TCP port 3389 should be Listening.
Method 4
Use the telnet tool to connect to the RDP port on the Remote Desktop server:
- From another computer, click Start, click Run, type cmd, and then click OK.
- At the command prompt, type
telnet <servername> 3389, where <servername> is the name of the Remote Desktop server, and then press Enter.
If telnet is successful, you receive the telnet screen and a cursor.
If telnet is not successful, you receive the following error message:
Connecting To servername... Could not open connection to the host, on port 3389: Connect failed
The qwinsta, netstat, and telnet tools are also included in Windows XP and Windows Server 2003. You can also download and use other troubleshooting tools, such as Portqry.
Resolution for Symptom 3
To resolve the issue, configure authentication and encryption.
To configure authentication and encryption for a connection, follow these steps:
On the RD Session Host server, open Remote Desktop Session Host Configuration. To open Remote Desktop Session Host Configuration, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, point to Remote Desktop Services, and then click Remote Desktop Session Host Configuration.
Under Connections, right-click the name of the connection, and then click Properties.
In the Properties dialog box for the connection, on the General tab, in Security layer, select a security method.
In Encryption level, click the level that you want. You can select Low, Client Compatible, High, or FIPS Compliant. See Step 4 above for Windows Server 2003 for Security layer and Encryption level options.
Note
- To perform this procedure, you must be a member of the Administrators group on the local computer, or you must have been delegated the appropriate authority. If the computer is joined to a domain, members of the Domain Admins group might be able to perform this procedure. As a security best practice, consider using Run as to perform this procedure.
- To open Remote Desktop Services Configuration, click Start, click Control Panel, double-click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Remote Desktop Services Configuration.
- Any encryption level settings that you configure in Group Policy override the configuration that you set by using the Remote Desktop Services Configuration tool. Also, if you enable the System cryptography: Use FIPS compliant algorithms for encryption, hashing, and signing Group Policy setting, this setting overrides the Set client connection encryption level Group Policy setting.
- When you change the encryption level, the new encryption level takes effect the next time a user logs on. If you require multiple levels of encryption on one server, install multiple network adapters and configure each adapter separately.
- To verify that certificate has a corresponding private key, in Remote Desktop Services Configuration, right-click the connection for which you want to view the certificate, click the General tab, click Edit, click the certificate that you want to view, and then click View Certificate. At the bottom of the General tab, the statement, You have a private key that corresponds to this certificate, should appear. You can also view this information by using the Certificates snap-in.
- The FIPS compliant setting (the System cryptography: Use FIPS compliant algorithms for encryption, hashing, and signing setting in Group Policy or the FIPS Compliant setting in Remote Desktop server Configuration) encrypts and decrypts data sent from the client to the server and from the server to the client, with the Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) 140-1 encryption algorithms, using Microsoft cryptographic modules. For more information, see Terminal Services in Windows Server 2003 Technical Reference.
- The High setting encrypts data sent from the client to the server and from the server to the client by using strong 128-bit encryption.
- The Client Compatible setting encrypts data sent between the client and the server at the maximum key strength supported by the client.
- The Low setting encrypts data sent from the client to the server using 56-bit encryption.
Additional troubleshooting step: Enable CAPI2 event logs
To help troubleshoot this problem, enable CAPI2 event logs on both the client and server computers. This command is shown in the following screenshot.
Workaround for the issue (You cannot completely disconnect a Remote Desktop server connection) described in Symptom 3
To work around this problem, follow these steps:
- Click Start, click Run, type gpedit.msc, and then click OK.
- Expand Computer Configuration, expand Administrative Templates, expand Windows Components, expand Remote Desktop Services, expand Remote Desktop Session Host, and then click Connections.
- In the right pane, double-click Configure keep-alive connection interval.
- Click Enabled, and then click OK.
- Close Group Policy Object Editor, click OK, and then quit Active Directory Users and Computers.
Resolution for Symptom 4
Important
This section, method, or task contains steps that tell you how to modify the registry. However, serious problems might occur if you modify the registry incorrectly. Therefore, make sure that you follow these steps carefully. For added protection, back up the registry before you modify it. Then, you can restore the registry if a problem occurs. For more information about how to back up and restore the registry, see 322756 How to back up and restore the registry in Windows.
To resolve this problem, back up and then remove the X509 Certificate registry keys, restart the computer, and then reactivate the Remote Desktop Services Licensing server. To do this, follow these steps.
Note
Perform the following procedure on each of the Remote Desktop servers.
Make sure that the Remote Desktop server registry has been successfully backed up.
Start Registry Editor.
Locate and then click the following registry subkey:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlTerminal ServerRCMOn the Registry menu, click Export Registry File.
Type exported- Certificate in the File name box, and then click *Save.
Note
If you have to restore this registry subkey in the future, double-click the Exported-parameters.reg file that you saved in this step.
Right-click each of the following values, click Delete, and then click Yes to verify the deletion:
- Certificate
- X509 Certificate
- X509 Certificate ID
- X509 Certificate2
Exit Registry Editor, and then restart the server.
References
For more information about Remote Desktop Gateway, see the following articles:
If this article does not help you resolve the problem, or if you experience symptoms that differ from those that are described in this article, visit the Microsoft Support for more information. To search your issue, in the Search support for help box, type the text of the error message that you received, or type a description of the problem.
-->Applies to: Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2
Now that you've set up the Remote Desktop client on your device (Android, Mac, iOS, or Windows), you may have questions. Here are answers to the most commonly asked questions about the Remote Desktop clients.
The majority of these questions apply to all of the clients, but there are a few client specific items.
If you have additional questions that you'd like us to answer, leave them as feedback on this article.
Setting up
Which PCs can I connect to?
Check out the supported configuration article for information about what PCs you can connect to.
How do I set up a PC for Remote Desktop?
I have my device set up, but I don't think the PC's ready. Help?
First, have you seen the Remote Desktop Setup Wizard? It walks you through getting your PC ready for remote access. Download and run that tool on your PC to get everything set.
Otherwise, if you prefer to do things manually, read on.
For Windows 10, do the following:
- On the device you want to connect to, open Settings.
- Select System and then Remote Desktop.
- Use the slider to enable Remote Desktop.
- In general, it's best to keep the PC awake and discoverable to facilitate connections. Click Show settings to go to the power settings for your PC, where you can change this setting.
Note
You can't connect to a PC that's asleep or hibernating, so make sure the settings for sleep and hibernation on the remote PC are set to Never. (Hibernation isn't available on all PCs.)
Make note of the name of this PC under How to connect to this PC. You'll need this to configure the clients.
You can grant permission for specific users to access this PC - to do that, click Select users that can remotely access this PC.Members of the Administrators group automatically have access.
For Windows 8.1, follow the instructions to allow remote connections in Connect to another desktop using Remote Desktop Connections.

Connection, gateway, and networks
Why can't I connect using Remote Desktop?
Here are some possible solutions to common problems you might encounter when trying to connect to a remote PC. If these solutions don't work, you can find more help on the Microsoft Community website.
The remote PC can't be found. Make sure you have the right PC name, and then check to see if you entered that name correctly. If you still can't connect, try using the IP address of the remote PC instead of the PC name.
There's a problem with the network. Make sure you have internet connection.
The Remote Desktop port might be blocked by a firewall. If you're using Windows Firewall, follow these steps:
Open Windows Firewall.
Click Allow an app or feature through Windows Firewall.
Click Change settings. You might be asked for an admin password or to confirm your choice.
Under Allowed apps and features, select Remote Desktop, and then tap or click OK.
If you're using a different firewall, make sure the port for Remote Desktop (usually 3389) is open.
Remote connections might not be set up on the remote PC. To fix this, scroll back up to How do I set up a PC for Remote Desktop? question in this topic.
The remote PC might only allow PCs to connect that have Network Level Authentication set up.
The remote PC might be turned off. You can't connect to a PC that's turned off, asleep, or hibernating, so make sure the settings for sleep and hibernation on the remote PC are set to Never (hibernation isn't available on all PCs.).
Why can't I find or connect to my PC?
Check the following:
Is the PC on and awake?
Did you enter the right name or IP address?
Important
Using the PC name requires your network to resolve the name correctly through DNS. In many home networks, you have to use the IP address instead of the host name to connect.
Is the PC on a different network? Did you configure the PC to let outside connections through? Check out Allow access to your PC from outside your network for help.
Are you connecting to a supported Windows version?
Note
Windows XP Home, Windows Media Center Edition, Windows Vista Home and Windows 7 Home or Starter are not supported without 3rd party software.
Why can't I sign in to a remote PC?
If you can see the sign-in screen of the remote PC but you can't sign in, you might not have been added to the Remote Desktop Users Group or to any group with administrator rights on the remote PC. Ask your system admin to do this for you.
Which connection methods are supported for company networks?
If you want to access your office desktop from outside your company network, your company must provide you with a means of remote access. The RD Client currently supports the following:
- Terminal Server Gateway or Remote Desktop Gateway
- Remote Desktop Web Access
- VPN (through iOS built-in VPN options)
VPN doesn't work
Microsoft Remote Desktop Connection 10
VPN issues can have several causes. The first step is to verify that the VPN works on the same network as your PC or Mac computer. If you can't test with a PC or Mac, you can try to access a company intranet web page with your device's browser.
Other things to check:
- The 3G network blocks or corrupts VPN. There are several 3G providers in the world who seem to block or corrupt 3G traffic. Verify VPN connectivity works correctly for over a minute.
- L2TP or PPTP VPNs. If you are using L2TP or PPTP in your VPN, please set Send All Traffic to ON in the VPN configuration.
- VPN is misconfigured. A misconfigured VPN server can be the reason why the VPN connections never worked or stopped working after some time. Ensure testing with the iOS device's web browser or a PC or Mac on the same network if this happens.
How can I test if VPN is working properly?
Verify that VPN is enabled on your device. You can test your VPN connection by going to a webpage on your internal network or using a web service which is only available via the VPN.
How do I configure L2TP or PPTP VPN connections?
If you are using L2TP or PPTP in your VPN, make sure to set Send all traffic to ON in the VPN configuration.
Web client
Which browsers can I use?
The web client supports Microsoft Edge, Internet Explorer 11, Mozilla Firefox (v55.0 and later), Safari, and Google Chrome.
What PCs can I use to access the web client?
The web client supports Windows, macOS, Linux, and ChromeOS. Mobile devices are not supported at this time.
Can I use the web client in a Remote Desktop deployment without a gateway?
No. The client requires a Remote Desktop Gateway to connect. Don't know what that means? Ask your admin about it.
Does the Remote Desktop web client replace the Remote Desktop Web Access page?
No. The Remote Desktop web client is hosted at a different URL than the Remote Desktop Web Access page. You can use either the web client or the Web Access page to view the remote resources in a browser.
Can I embed the web client in another web page?
This feature is not supported at the moment.
Monitors, audio, and mouse
How do I use all of my monitors?
To use two or more screens, do the following:
- Right-click the remote desktop that you want to enable multiple screens for, and then click Edit.
- Enable Use all monitors and Full screen.
Is bi-directional sound supported?
Bi-directional sound can be configured in the Windows client on a per-connection basis. The relevant settings can be accessed in the Remote audio section of the Local Resources options tab.
What can I do if the sound won't play?
Sign out of the session (don't just disconnect, sign all the way out), and then sign in again.
Mac client - hardware questions
Is retina resolution supported?
Yes, the remote desktop client supports retina resolution.
How do I enable secondary right-click?
In order to make use of the right-click inside an open session you have three options:
- Standard PC two button USB mouse
- Apple Magic Mouse: To enable right-click, click System Preferences in the dock, click Mouse, and then enable Secondary click.
- Apple Magic Trackpad or MacBook Trackpad: To enable right-click, click System Preferences in the dock, click Trackpad, and then enable Secondary click.
Is AirPrint supported?
No, the Remote Desktop client doesn't support AirPrint. (This is true for both Mac and iOS clients.)
Why do incorrect characters appear in the session?
If you are using an international keyboard, you might see an issue where the characters that appear in the session do match the characters you typed on the Mac keyboard.
This can occur in the following scenarios:
- You are using a keyboard that the remote session does not recognize. When Remote Desktop doesn't recognize the keyboard, it defaults to the language last used with the remote PC.
- You are connecting to a previously disconnected session on a remote PC and that remote PC uses a different keyboard language than the language you are currently trying to use.
Microsoft Remote Desktop Unable To Connect To Remote Pc
You can fix this issue by manually setting the keyboard language for the remote session. See the steps in the next section.
How do language settings affect keyboards in a remote session?
There are many types of Mac keyboard layouts. Some of these are Mac specific layouts or custom layouts for which an exact match may not be available on the version of Windows you are remoting into. The remote session maps your keyboard to the best matching keyboard language available on the remote PC.
If your Mac keyboard layout is set to the PC version of the language keyboard (for example, French – PC) all your keys should be mapped correctly and your keyboard should just work.
If your Mac keyboard layout is set to the Mac version of a keyboard (for example, French) the remote session will map you to the PC version of the French language. Some of the Mac keyboard shortcuts you are used to using on OSX will not work in the remote Windows session.
If your keyboard layout is set to a variation of a language (for example, Canadian-French) and if the remote session cannot map you to that exact variation, the remote session will map you to the closest language (for example, French). Some of the Mac keyboard shortcuts you are used to using on OSX will not work in the remote Windows session.
If your keyboard layout is set to a layout the remote session cannot match at all, your remote session will default to give you the language you last used with that PC. In this case, or in cases where you need to change the language of your remote session to match your Mac keyboard, you can manually set the keyboard language in the remote session to the language that is the closest match to the one you wish to use as follows.
Use the following instructions to change the keyboard layout inside the remote desktop session:
On Windows 10 or Windows 8:
- From inside the remote session, open Region and Language. Click Start > Settings > Time and Language. Open Region and Language.
- Add the language you want to use. Then close the Region and Language window.
- Now, in the remote session, you'll see the ability to switch between languages. (In the right side of the remote session, near the clock.) Click the language you want to switch to (such as Eng).
You might need to close and restart the application you are currently using for the keyboard changes to take effect.
Specific errors
Why do I get an 'Insufficient privileges' error?
You are not allowed to access the session you want to connect to. The most likely cause is that you are trying to connect to an admin session. Only administrators are allowed to connect to the console. Verify that the console switch is off in the advanced settings of the remote desktop. If this is not the source of the problem, please contact your system administrator for further assistance.
Why does the client say that there is no CAL?
When a remote desktop client connects to a Remote Desktop server, the server issues a Remote Desktop Services Client Access License (RDS CAL) stored by the client. Whenever the client connects again it will use its RDS CAL and the server will not issue another license. The server will issue another license if the RDS CAL on the device is missing or corrupt. When the maximum number of licensed devices is reached the server will not issue new RDS CALs. Contact your network administrator for assistance.
Why did I get an 'Access Denied' error?
The 'Access Denied' error is a generated by the Remote Desktop Gateway and the result of incorrect credentials during the connection attempt. Verify your username and password. If the connection worked before and the error occurred recently, you possibly changed your Windows user account password and haven't updated it yet in the remote desktop settings.
What does 'RPC Error 23014' or 'Error 0x59e6' mean?
In case of an RPC error 23014 or Error 0x59E6 try again after waiting a few minutes, the RD Gateway server has reached the maximum number of active connections. Depending on the Windows version running on the RD Gateway the maximum number of connections differs: The Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard implementation limits the number of connections to 250. The Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation implementation limits the number of connections to 50. All other Windows implementations allow an unlimited number of connections.
What does the 'Failed to parse NTLM challenge' error mean?
This error is caused by a misconfiguration on the remote PC. Make sure the RDP security level setting on the remote PC is set to 'Client Compatible.' (Talk to your system admin if you need help doing this.)
What does 'TS_RAP You are not allowed to connect to the given host' mean?
This error happens when a Resource Authorization Policy on the gateway server stops your user name from connecting to the remote PC. This can happen in the following instances:
- The remote PC name is the same as the name of the gateway. Then, when you try to connect to the remote PC, the connection goes to the gateway instead, which you probably don't have permission to access. If you need to connect to the gateway, do not use the external gateway name as PC name. Instead use 'localhost' or the IP address (127.0.0.1), or the internal server name.
- Your user account isn't a member of the user group for remote access.
